In digital circuits, a flip-flop is a term referring to an electronic circuit that has two stable states and thereby is capable of serving as one bit of memory. Today, the term flip-flop has come to mostly denote non-transparent (clocked or edge-triggered) devices, while the simpler transparent ones are often referred to as latches; however, as this distinction is quite new, the two words are sometimes used interchangeably.
A flip-flop is usually controlled by one or two control signals and/or a gate or clock signal. The output often includes the complement as well as the normal output. As flip-flops are implemented electronically, they require power and ground connections.
These truth tables describe how the outputs of a given flip flop will be determined by a combination of inputs. Not shown are Preset and Clear inputs, which will cause the "Q" outputs to be set high or low, respectively.
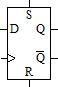
D.FLIP-FLOP
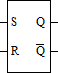
SR FLIP-FLOP
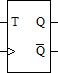
T FLIP-FLOP
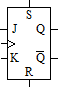
JK FLIP-FLOP
Information :
|